Global growth remains steady but below historical averages, according to the IMF’s latest forecast, released on Friday, January 17, in Washington, DC.

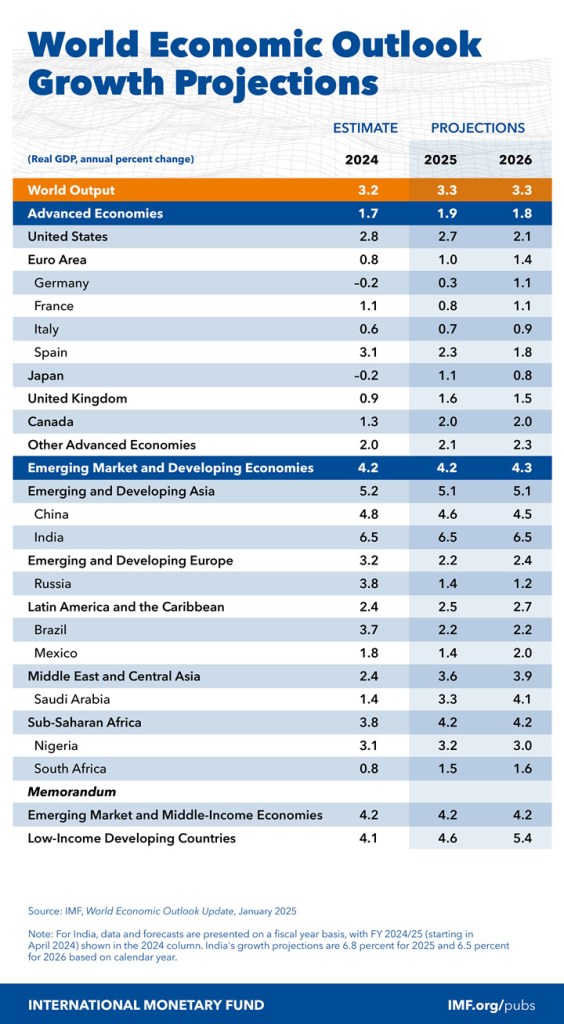
Washington, DC, January 17, 2025 — Inflation is gradually aligning with the targets set by central banks, while economic growth remains stable at 3.3%. Nonetheless, the International Monetary Fund has indicated that risks and uncertainties persist ahead of the forthcoming quarterly update to the World Economic Outlook.
“Global economic growth is projected to remain steady at 3.3% this year and the next, reflecting a diminished potential growth following the pandemic. Inflation rates are steadily declining, with estimates indicating a reduction to 4.2% this year and 3.5% in the subsequent year, thereby moving closer to the targets set by central banks. This period signifies the conclusion of an economic cycle and the commencement of a new one. Nevertheless, disparities among countries continue to widen. The United States economy surpasses expectations due to robust domestic demand, whereas Europe is grappling with sluggish growth and persistently elevated energy prices. In contrast, emerging markets demonstrate resilience, with China anticipated to undergo a modest economic recovery,” remarked Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas, Chief Economist and Director of Research at the International Monetary Fund, before the report’s release.


The divergence indicates that key economies like China, Europe, and the U.S. face distinct challenges.
“Significant risks include a potential acceleration of the economic slowdown in Europe, driven by escalating energy costs and concerns regarding public debt. Additionally, inadequate policy support in China could lead to a stagnation trap. In the United States, shifts in fiscal and trade policy, along with possible restrictions on immigration, may interact with an anticipated confidence boost resulting from expected deregulation. These factors could exert opposing influences on economic output; however, collectively, they are likely to elevate inflationary pressures, necessitating a tighter monetary policy. Such dynamics could impose challenges on emerging markets through the constriction of financial conditions and the strengthening of the U.S. dollar,” stated Gourinchas.

What actions can policymakers take? The IMF has offered three key recommendations for them to consider:
- Monetary policy must exhibit adaptability to effectively address inflationary risks while safeguarding the stability of economic expectations.
- Establishing a more robust fiscal policy foundation is crucial, necessitating executing credible consolidation efforts as appropriate.
- Implementing structural reforms simultaneously is essential for sustaining growth throughout this adjustment process. These reforms should be strategically directed towards fostering innovation and enhancing competition.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has provided the following policy recommendations for emerging markets:
- Flexible exchange rates and targeted fiscal and monetary measures are essential for the stability of these economies.
- Furthermore, the Fund emphasizes the significance of collaboration in international trade for fostering growth and overall well-being.
- Enhanced multilateral cooperation, particularly in trade policy, is vital for constructing a resilient global economy.
Source: IMF
— The CitiTimes editor is a financial market analyst with an IMF academic certificate.

